
Mastering Total Dynamic Head Calculations
TDH plays a crucial role in determining how efficiently water moves through a system, impacting performance, energy consumption and long-term maintenance costs.
Choosing the right pump for your pool or spa is more than just horsepower, it requires a precise understanding of Total Dynamic Head (TDH). TDH represents the total height a pump must overcome to effectively move the water in a pool or spa’s recirculating system, encompassing both the vertical rise and the resistance due to friction loss.
TDH plays a crucial role in determining how efficiently water moves through a system, impacting performance, energy consumption and long-term maintenance costs.
Furthermore, TDH calculations are paramount for ensuring compliance with the International Swimming Pool and Spa Code® (ISPSC), the Virginia Graeme Baker Pool and Spa Safety Act (VGBA), the 2021 ANSI/PHTA/ICC-15 American National Standard for Residential Swimming Pool and Spa Energy Efficiency and the 2017 ANSI/PHTA/ICC-16 American National Standard for Suction Outlet Fitting Assemblies (SOFA) for Use in Pools, Spas and Hot Tubs.
Key Components of Total Dynamic Head
- Static Head: This includes the vertical distance between the water source and the discharge point.
- Static Suction Head (SSH): The elevation drops from the water source to the pump.
- Static Discharge Head (SDH): The elevation rises from the pump to the discharge point.
- Friction Losses: These occur due to resistance within the piping system, including fittings and valves. Friction losses can vary significantly based on the type, length and complexity of your piping. Calculating these losses is essential for precise results.
- Miscellaneous Losses: These are additional TDH losses caused by fittings that create turbulence and obstructions in the flow, such as elbows, valves, filters, heaters, etc.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Total Dynamic Head
To calculate TDH, use the following formula: TDH = Static Head + Friction Losses + Miscellaneous Losses
Where:
- Static Head= SSH + SDH
- Friction Losses can be expressed in feet or meters of fluid.
Identify the Static Head
- Measure the distance from the water source to the pump (SSH) and the pump to the discharge point (SDH). For instance, if your SSH is 10 feet and SDH is 20 feet, your Static Head would be.
- Static Head = 10 feet + 20 feet = 30 feet
-
Calculate Friction Losses
- Utilize the appropriate formula to assess friction losses based on factors like pipe diameter, length, flow rate and the nature of the fluid. All pipe manufacturers have friction loss charts based on the pipe.
- Let’s say the calculated friction loss here turns out to be 5 feet.
-
Factor in Miscellaneous Losses
- Consider any additional head losses from fittings and valves, filters, pool heaters/boilers and solar heat exchangers:
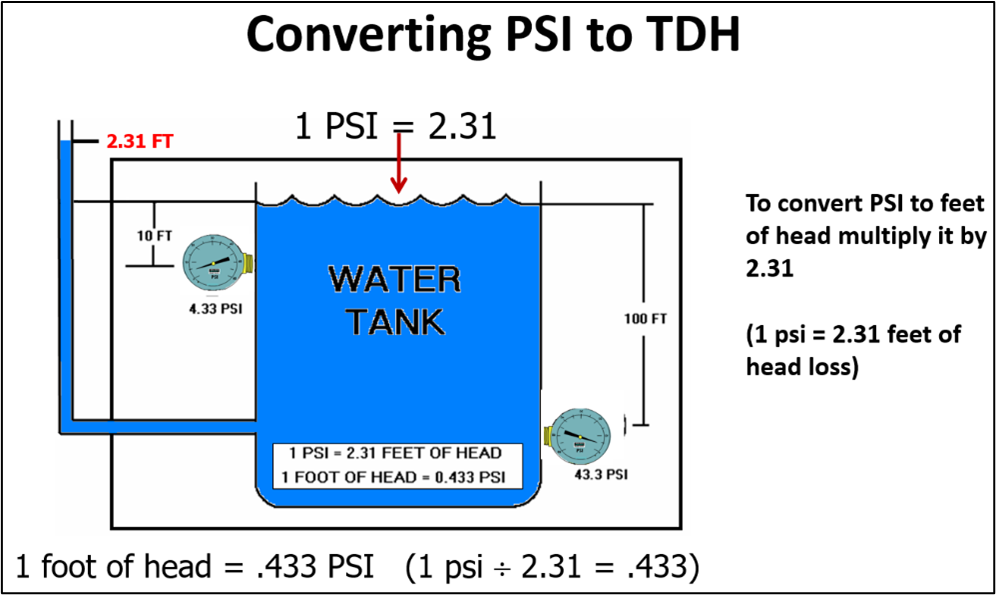
- Fittings, valves, filters, pool heaters/boilers, and solar heat exchangers express the loss in PSI for the U.S. market. To convert PSI to TDH, we need to do a little math. Based on the specific gravity of water at sea level, we need to multiply the PSI pressure loss by 2.31 to get our TDH (PSI x 2.31 = TDH).
- Let’s say the calculated Miscellaneous Loss is around 3 feet.
Combine Values in the TDH Formula:
- TDH = Static Head + Friction Losses + Miscellaneous Losses
- TDH = 30 feet + 5 feet + 3 feet = 38 feet
Why Total Dynamic Head Calculations Matter
Effective Pump Selection
By accurately gauging the necessary TDH, you can choose a pump that meets your system’s demands, ensuring reliable operation, safeguarding against premature failures and ensuring safety compliance. To do this, we need to look at the pump curve or how many gallons per minute the pump will be capable of producing at the designed TDH. Any pool pump rated at or above 1 HP will utilize variable speed technology.
It is important to note that when the pump operates at full speed, the gallons per minute (GPM) cannot exceed the maximum flow rate embossed on the suction outlet fitting assembly (SOFA). The pump must operate between the required GPM for the turnover rate and at or below the SOFA GPM rating.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Proper TDH assessments can significantly reduce energy consumption, maximize cost savings and optimize productivity.
Superior System Design
Pool and spa engineers/designers benefit greatly from a comprehensive understanding of TDH requirements, allowing them to develop piping systems that perform exceptionally while minimizing operational problems.
Ensuring Efficient and Effective Pump Operation
TDH calculations are not just another technical detail; they are a critical factor that can make or break turnover rates and suction entrapment avoidance.
By mastering each aspect of TDH and conducting precise calculations, you’ll not only ensure efficient and effective pump operation, but also secure long-lasting results tailored to your specific needs.
For in-depth ISPSC training, don’t hesitate to contact ICC training to schedule your class now, email training by clicking here or calling 888-422-7233 ext. 33818.
To stay updated on the latest PMG industry news, subscribe to the Code Council’s PMG newsletter here.







