
Code Corner: 2024 International Fuel Gas Code Chapter 3: General Regulations
The Code Corner, explores sections of the I-Codes each month, focusing on key elements of these essential codes. This month, we’re spotlighting the scope of Chapter 3 of the 2024 International Fuel Gas Code: General Regulations
The International Codes® (I-Codes), developed by the International Code Council, are a family of fifteen coordinated, modern building safety codes that help ensure the design and construction of safe, sustainable and affordable structures.
The I-Codes are the most widely adopted set of model codes globally, implemented in all 50 U.S. states and many countries around the world.
The Building Safety Journal’s series, Code Corner, explores sections of the I-Codes each month, focusing on key elements of these essential codes. This month, we’re spotlighting the scope of Chapter 3 of the 2024 International Fuel Gas Code® (IFGC): General Regulations.
International Fuel Gas Code 307.2 Fuel-burning Appliances
Liquid combustion byproducts of condensing appliances shall be collected and discharged to an approved plumbing fixture or disposal area in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Condensate piping shall be of approved corrosion-resistant material and shall be not smaller than the drain connection on the appliance. Such piping shall maintain a minimum slope in the direction of discharge of not less than 1/8 unit vertical in 12 units horizontal (1 percent slope). The termination of concealed condensate piping shall be marked to indicate whether the piping is connected to the primary drain or to the secondary drain.
This section of the IFGC contains detailed requirements for the disposal of condensate from appliances such as condensing furnaces, boilers and water heaters. Condensation must be collected from appliances and equipment in accordance with the manufacturer’s installation instructions and this section. High-efficiency condensing-type appliances and some mid-efficiency appliances produce water as a combustion byproduct. This condensate is collected at various points in the appliance heat exchangers and venting system and must be disposed of. Because of impurities in the fuel and combustion air, the condensate can be acidic and thus corrosive to many materials.
For example, such condensate can contain hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, although the acid solution would be weak. The slope requirement promotes drainage and prohibits low points (dips) in the piping that would trap water and air that would impede flow.
Section 307.2 requires a primary condensate drainage system, and Section 307.5 requires an auxiliary drain pan and drain where overflow of the primary drain would cause damage to the building. Where the two drain lines serving the same remote appliance are not readily observable, one would not know which drain line was which.
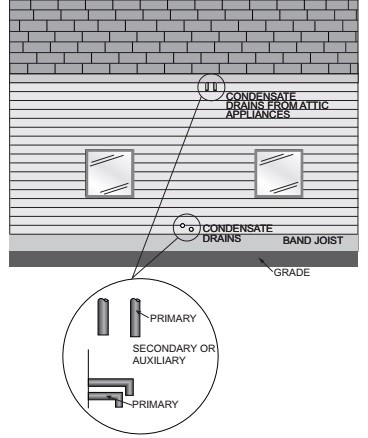
For example, if the two drain lines came from an attic space and terminated through an outside wall, one could not discern which was the primary drain. If condensate is flowing from the auxiliary drain, that is an indication of a failed primary drain line, and immediate attention would be needed to correct the problem. If the two drain lines were not labeled as to their purpose, it would not be possible to distinguish between normal primary drain line flow and abnormal auxiliary drain line flow. The required marking is intended to be permanent; therefore, it must be suitable for the location to remain visible for the life of the system. Duct tape and a felt tip pen marking would not survive long when exposed to the weather (see Commentary Figure 307.2).
To learn more about the Code Council’s IPSDC, click here. To stay updated on the latest PMG industry news, subscribe to the Code Council’s PMG newsletter here.






