
Code Corner: 2024 International Mechanical Code Chapter 4: Ventilation
The Code Corner, explores sections of the I-Codes each month, focusing on key elements of these essential codes. This month, we’re spotlighting the scope of Chapter 4 of the 2024 International Mechanical Code®: Ventilation.
The International Codes® (I-Codes), developed by the International Code Council, are a family of fifteen coordinated, modern building safety codes that help ensure the design and construction of safe, sustainable and affordable structures.
The I-Codes are the most widely adopted set of model codes globally, implemented in all 50 U.S. states and many countries around the world.
The Building Safety Journal’s series, Code Corner, explores sections of the I-Codes each month, focusing on key elements of these essential codes. This month, we’re spotlighting the scope of Chapter 4 of the 2024 International Mechanical Code® (IMC): Ventilation.

International Mechanical Code 402.1 Natural Ventilation
Natural ventilation of an occupied space shall be through windows, doors, louvers or other openings to the outdoors. The operating mechanism for such openings shall be provided with ready access so that the openings are readily controllable by the building occupants.
This section of the IMC presents the standard of natural ventilation for all occupied spaces. Natural ventilation is dependent on many factors and variables including, the indoor and outdoor temperatures, the wind speed and direction, the location and distribution of openings to the outdoors, the configuration of the openings, the location of adjacent buildings, the height of the building and the uncertainty factor of the human behavior required to open any or all openings to the outdoors.
Openings to the outdoor air, such as doors, windows, louvers, etc., provide natural ventilation. The section does not, however, state or intend that the doors, windows or openings actually be constantly open. The intent is that they be maintained in an operable condition so that they are available for use at the discretion of the occupant.
Section 402 is consistent with International Building Code® (IBC) Section 1202.5. See IBC Section 1202.5.2.1, which requires mechanical ventilation in rooms that contain bathing fixtures. Bathtubs, showers, spas and similar bathing fixtures add moisture to the indoor air that must be controlled to prevent unhealthy conditions and damage to building components.
International Mechanical Code 402.2 Ventilation Area Required
The minimum openable area to the outdoors shall be 4% of the floor area being ventilated.
This section specifies the ratio of openable doors, windows and other openings to the floor space being ventilated but does not address the distribution around the space or location of these openings. Nor does the code address the configuration of openings such as the various types of windows.
It is the designer’s responsibility to distribute openings to accomplish the natural ventilation of the space. The placement of ventilation openings should be planned to induce airflow through the space. For example, placing all openings on the same wall will probably not be as effective as placing openings on opposite walls.
Where inadequate natural ventilation is provided, mechanical ventilation can supplement any inadequacy (see Section 403). The plan reviewer can determine compliance with this section.
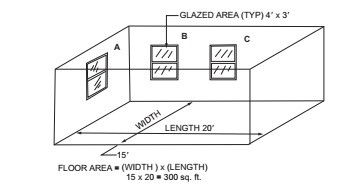
For example, in Commentary Figure 402.2, the combined openable area (the net free area of a door, window, louver, vent or skylight, etc., when fully open) of double-hung Windows B and C is equal to 4 percent of the floor area [300 × 0.04 = 12 square feet (1.1 m2)]. Note that only half of the area of the double-hung windows is considered to be openable. The openable area of Window A is not required and need not open onto a court or yard complying with IBC Section 1206.
To learn more about the Code Council’s IMC, click here. To stay updated on the latest PMG industry news, subscribe to the Code Council’s PMG newsletter here.






