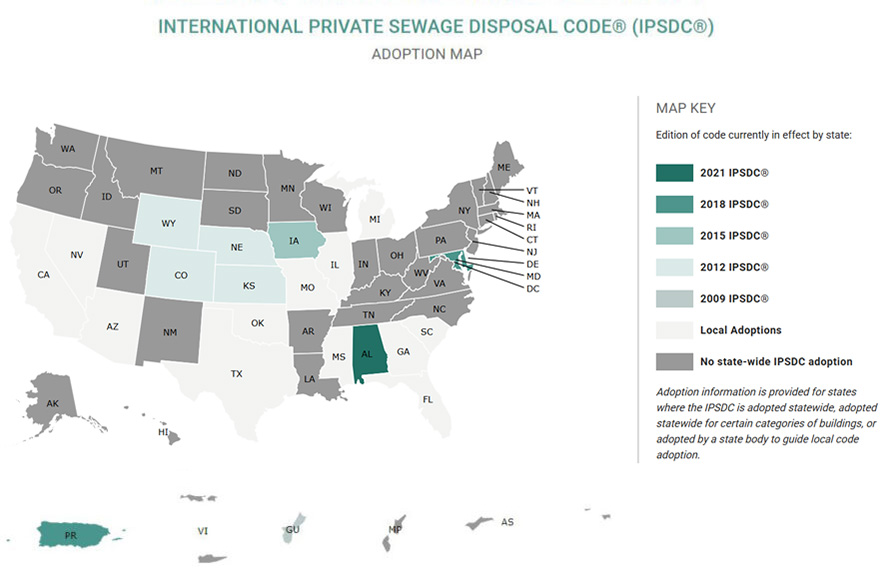
The IPSDC is an innovative, efficient and effective private sewage disposal code that is fully correlated with the other International Codes® (I-Codes®). It includes provisions for the design, installation, and inspection of private sewage disposal systems, and provides flexibility in the development of safe systems. The IPSDC is adopted in 17 states across the U.S. and is also adopted in Puerto Rico and Guam. Approximately 131 million people, or 38% of the US population, live in areas that have adopted the IPSDC.
The IPSDC is a vital part of a complete building safety system for communities, individuals, and businesses needing their own onsite wastewater solutions. It is a companion to the IPC that provides minimum acceptable requirements for private sewage disposal systems in order to protect humans and the environment from insanitary conditions.
The I-Codes, when adopted as a family of codes, correlating as they do, provide a consistent system of regulations that designers, builders, and regulators can rely on, across city, county, or state lines.
The adoption of building codes, including the private sewage disposal code, is not just about the codes. Technical support, in the form of expert advice, code opinions, and technical resources are some of the most sought-after services following adoption of a code.
The Code Council’s expert technical staff provides advice, code opinions, and resources to our more than 60,000 members as a complimentary benefit.
We have several resources, including commentaries and study companions, to support our members and industry professionals in achieving a better understanding of the code and implementing inspection programs.
Numerous training resources are available on the IPSDC including face to face training and webinars which are led by qualified instructors and industry leaders.
The Code Council also has a world class digital platform where codes, industry standards and resources can be accessed from one’s computer, tablet, or phone.
The IPSDC is developed through a governmental consensus process
that involves many interest groups including public safety officials, plumbing contractors, manufacturers, standards development organizations, academia, consumers and many more;
cannot be influenced by vested financial interests;
and is conducted every three years.