Advancements in the Implementation of Hydrogen Fuel
Amongst global efforts to combat greenhouse gas emissions, hydrogen fuel has emerged as a viable solution in transitioning to a more sustainable and climate-friendly fuel source.
Because of its ability to be produced with zero or near-zero carbon emissions, many regions have begun investing in hydrogen technologies, which has further accelerated industry innovation and job opportunities on a global scale.
Accelerating Hydrogen Fuel Deployment Through H2Hubs
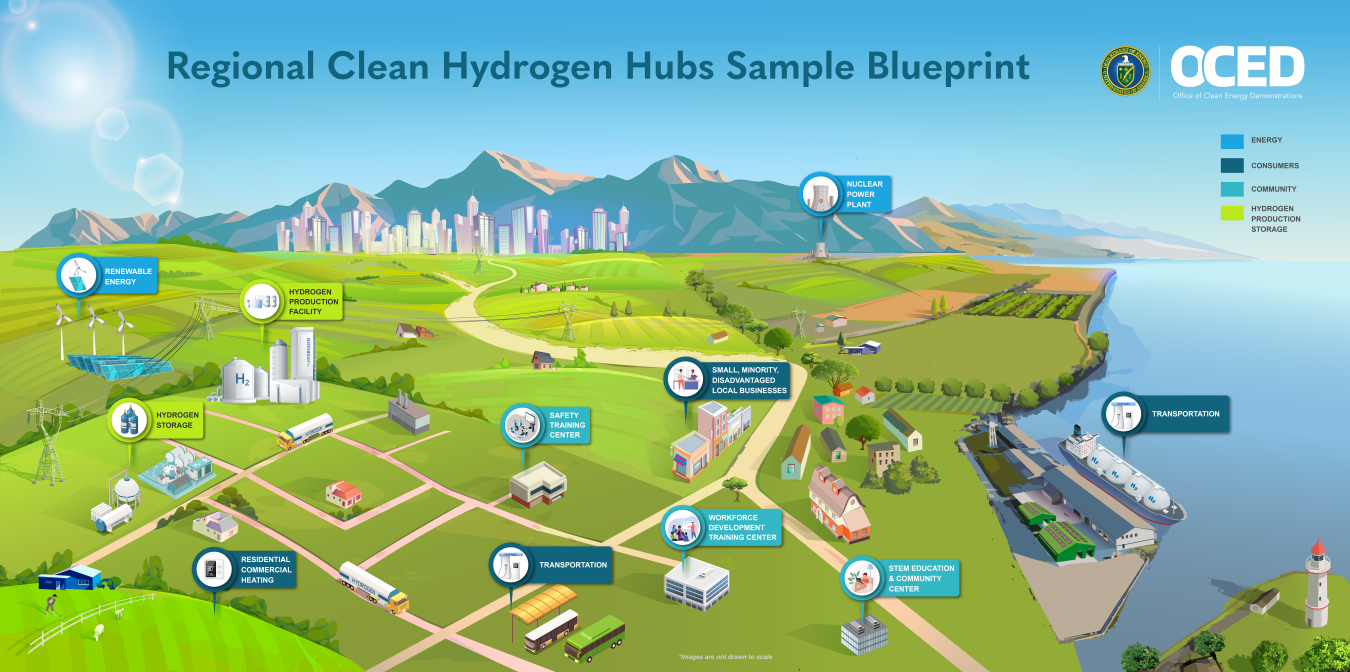
On October 13th, 2023, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced the allocation of $7 billion dollars to develop seven Regional Clean Hydrogen Hubs (H2 Hubs) strategically located across the U.S. as part of the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
The H2Hubs will accelerate the commercial-scale deployment of low-cost hydrogen to meet the nation’s climate and energy security goals.
The H2Hubs are anticipated to generate a combined output of three million metric tons of hydrogen each year, contributing to almost one-third of the 2030 U.S. production goal while reducing emissions from hard-to-decarbonize industrial sectors.
Additionally, the H2Hubs are projected to decrease carbon dioxide emissions by 25 million metric tons annually, as well as generate and maintain tens of thousands of jobs nationwide while promoting healthier communities.
Hydrogen Fuel Provisions in the I-Codes
Model codes and standards must be updated to address safety gaps when hydrogen is blended into the natural gas supply. The Code Council is currently in the process of developing the 2027 International Codes® (I-Codes), which includes code proposals developed by the PMG and Fire Code Action Committees that address the blending of gaseous hydrogen with natural gas in the built environment.
Gaseous hydrogen fuel at least 95 percent by volume and no more than 1 percent oxygen, has had code requirements included in the International Fuel Gas Code® (IFGC®) and many other publications for years. The working group’s scope was to expand the minimum safety provisions to address natural gas including gaseous hydrogen admixtures.
Hydrogen Working Group
The PMGCAC Hydrogen Working Group was composed of representatives from academia, national and international associations, national testing laboratories, manufacturers of appliances/equipment/piping systems, contractors, engineers, natural gas energy suppliers, standard development organizations, building and fire officials and other stakeholders.
This group assessed existing I-Code requirements related to hydrogen use, considering current industry practices and safety needs in the built environment.
Through collaborative efforts, rigorous code proposal development and proactive regional outreach, the Code Council is ensuring codes address the global paradigm shift towards a safer, more sustainable and efficient hydrogen-fueled future.
Hydrogen Fuel FAQs
Learn More About Hydrogen Fuel
Background Information
- Background on hydrogen use as a carbon free fuel
Read article - Background on the regional clean hydrogen hubs
Read article
Other Hydrogen Fuel Resources
- Read about bringing heat-reaction technology to the U.S.
- Learn more about the development of the I-Codes
- Get an overview of our PMG Codes
- For more information on the progress of hydrogen utilization in the U.S. and globally, visit the Department of Energy's Hydrogen Program website
Hydrogen Codes and Standards Development
The Code Council actively engages in opportunities to support hydrogen codes and standards development. Some of these activities include:
Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Energy Association (FCHEA) National Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Codes and Standards Coordinating Committee – Member
Read details▼
- Through this committee, the Code Council advises the DOE on hydrogen advancements in research, development and technology for U.S. Clean Hydrogen Strategy Road Mapping
- Members of this committee include the Code Council, National Research Labs, CSA, ASTM, ASME, DOE, EPA, NFPA, multiple state natural gas supplier companies, Authorities Having Jurisdiction, academia and manufacturers
Development of Canada’s National Hydrogen Deployment Codes and Standards Roadmap through Standards Council of Canada and National Resources Canada – Committee Task Group Member
As an active member of the Center for Hydrogen Safety (CHS), the Code Council is involved in developing tools and best practices to address several education gaps related to hydrogen production, storage, transportation and end-use. This involvement extends to both national and international levels. Specifically, the Code Council focuses on developing permitting and inspection guidance for H2 projects, along with training programs covering hydrogen manufacturing, transportation, storage and usage, among other aspects of guidance development.
CHS Culture Working Group – Participant
NFPA 2 Hydrogen Technologies Code Technical Committee – Member
ASTM D03 Gaseous Fuels Main Committee – Member
ASTM D03.14 Subcommittee for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells assisting in the development of gaseous hydrogen related standards – Committee Member
Read details▼
Served as panelist at ASTM Natural Gas Hydrogen Blends Workshop Dec. 5-6, 2023, performing presentations on codes and standards associated with the use of hydrogen
ASTM D7606-17 Standard Practice for Sampling of High-Pressure Hydrogen and Related Fuel Cell Feed Gases – Committee Member
Code Council PMGCAC H2 – Working Group Liaisons
Center for Hydrogen Safety (CHS) Hydrogen Hubs Working Group
Read details▼
Worldwide, there's a noteworthy surge in activities and substantial funding allocated toward advancing hydrogen hubs.
As these initiatives proceed, there will naturally arise inquiries about safety protocols and optimal practices. In the realm of hydrogen safety, the preeminent global authority is the Center for Hydrogen Safety (CHS). To meet the needs of these developing hubs CHS is establishing a Hydrogen Hubs Working Group that will be open to any CHS member that is a part of a global hub.
The Hydrogen Hubs Working Group will provide a forum for hub participants to:
- Discuss safety topics and issues
- Participate in a community to resolve shared problems.
- Develop resources that can be used among working group members
- Highlight and promote significant hydrogen safety issues to outside entities
Technical committee member for the following appliance and equipment standards developing requirements for blended H2 and natural gas
Read details▼
- ANSI/CSA Z21 and Z83 Joint Technical Committee members addressing H2 and Natural Gas blending standards for appliances and equipment
- CSA Z21.83 Gas Fueled Products and Related Accessories
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - H2 test gas composition and compatibility/flashback/burner characteristics
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Piping Systems and Higher Pressures
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Impact on Venting Materials (Metallic and Non-Metallic)/Heat Exchangers
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Piping Systems/Threaded Connections (for end use)
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Retroactivity/Inservice Appliances
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Controls/Internal-External Leakage - Vent Limiting Function
- CSA Z21/83 H2 Level 2 Subgroup - Test Gas Composition/Gas Compatibility Limits
- CSA Vented Heaters TSC (J101.22)
- Z21.50/CSA 2.22, Vented decorative gas appliances
- Z21.86/CSA 2.32, Vented gas-fired space heating appliances
- Z21.88/CSA 2.33, Vented gas fireplace heaters
- CSA Unvented Heaters TSC (U101.2)
- Z21.11.2, Gas-fired room heaters, volume II, unvented room heaters
- Z21.11.3, Gas-fired room heaters, volume III, propane-fired portable emergency use heater systems
- Z21.76, Gas-fired unvented catalytic room heaters for use with propane gas
- Z21.91, Ventless firebox enclosures for gas-fired unvented gas log type room heaters
- CSA Infrared Heaters TSC (J101.4)
- Z83.19/CSA 2.35, Gas-fired high-intensity infrared heaters
- Z83.20/CSA 2.342, Gas-fired tubular, and low-intensity infrared heaters
- Z83.26/CSA 2.37, Gas-fired outdoor infrared patio heaters
- CSA 2.20 (draft), Gas-fired brooders
- CSA/ANSI LC 1 Fuel Gas Piping Systems Using Corrugated Stainless-Steel Tubing (CSST)
- CSA/ANSI LC 4 Press‐connect metallic fittings for use in fuel gas distribution systems
- CSA/ANSI LC 6 Natural Gas Operated Diaphragm Pumps
- CSA/ANSI Z21.41- CSA 6.9, Quick-disconnect devices for use with gas fuel appliances
- CSA/ANSI Z21.66 - CSA 6.14 - Automatic damper devices for use with gas-fired appliances
- CSA/ANSI Z21.21/CSA 6.5 - Automatic valves for gas appliances
- CSA/ANSI Joint Technical Sub-Committee on Standards on Automatic Gas Controls [J101.7]
- CSA/ANSI Joint Technical Sub-Committee on Standards on Manual Valves [J101.16]
- CSA Technical Sub-Committee JB 121.17 Performance Testing of Hydrogen-Enriched Appliances (P.17)
Talk to an Expert
For more information, contact Mark Fasel Director of PMG Technical Resources at mfasel@iccsafe.org.